Hello,
I am doing some morphological image processing. I want to remove the 4 unwanted blobs from the binary object(image below)
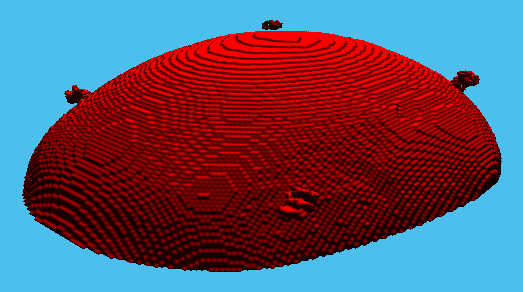
If I axially slice the image, I can take the largest connected component and exclude others like the image below:

I have tried the following codes which results binary size mismatch issues.
ind = 1;
sz = size(bi) % bi is the 3D mask with dimension: 170x256x100
final_mask = zeros(sz)
for i = 1:sz(3) %taking the 2D axial slice iterations-> 1:100
cc = bwconncomp(bi(:,:,i));
% disp(cc)
S = regionprops(cc, 'Area', 'PixelIdxList');%'Centroid');
ax_slice = zeros(sz(1), sz(2));
numPixels = cellfun(@numel, cc.PixelIdxList);
% disp(numPixels)
[biggest,idx] = max(numPixels); % taking the largest component number of pixels and their indices
ax_slice(cc.PixelIdxList{idx})= 1;
final_mask(:,:,i) = ax_slice;
endPlease let me know how to deal with it.
NOTE:-
Matlabsolutions.com provide latest MatLab Homework Help,MatLab Assignment Help for students, engineers and researchers in Multiple Branches like ECE, EEE, CSE, Mechanical, Civil with 100% output.Matlab Code for B.E, B.Tech,M.E,M.Tech, Ph.D. Scholars with 100% privacy guaranteed. Get MATLAB projects with source code for your learning and research.
- erode image
- dilate image
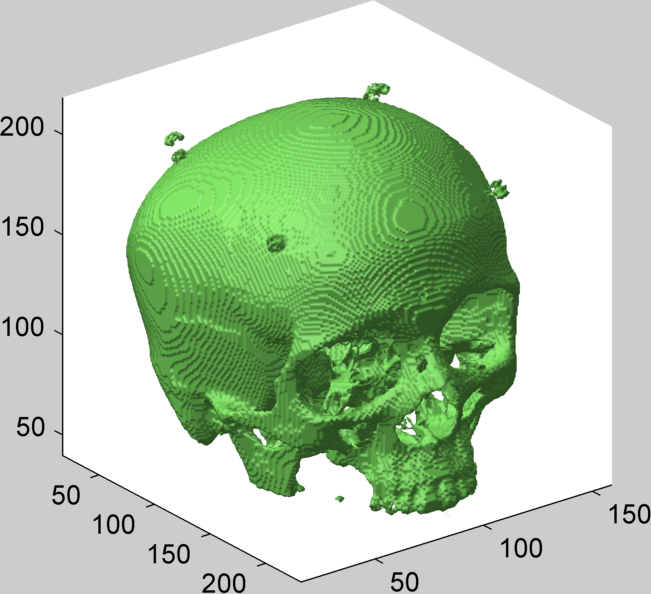
clc % clear command window cla % clear axes bi11 = bi; % create copy of 'bi' bi1 = bi(:,:,170:end); % get top part R = 2; % radius of structuring element [x,y,z] = meshgrid(-R:R); % X Y Z 3d matrices el = x.^2+y.^2+z.^2 <= R^2; % sphere of radius 'R' bi2 = imerode(bi1, el); % erode image bi3 = imdilate(bi2, el); % dilate image bi11(:,:,170:end) = bi3; % replace original top part isosurface(bi11,.95) % display 3d image axis vis3d light
Comments
Post a Comment